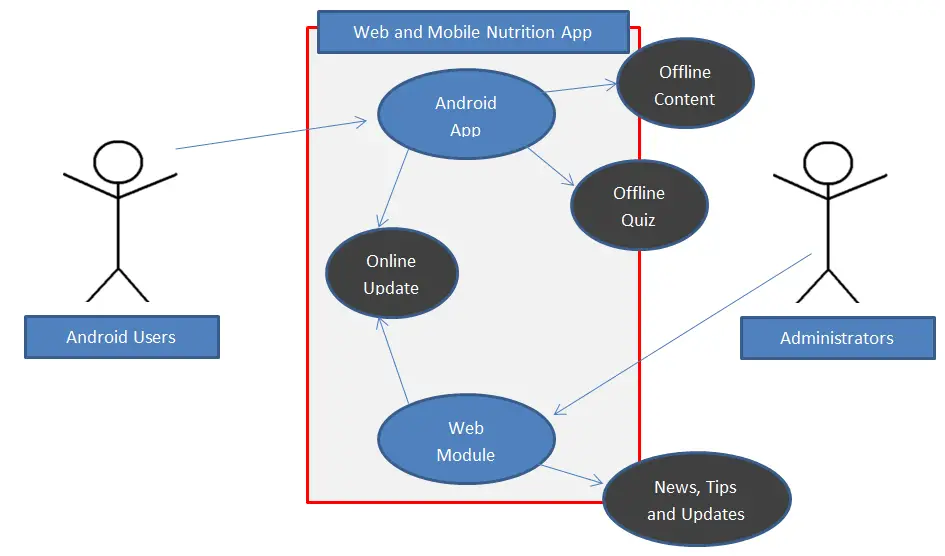
Financial Management System Review of Related Literature
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this section we will compare the foreign and local studies and systems of some companies and authors in order to get some detailed information that will help for building a screen design, business case, and also to determine the possible features that we need to add in our system and the most important thing is we determine our uniqueness to the existing system.

Related Foreign Studies:
Fundamental of Financial Management,
Based on Brigman (2007)
Based on Brigman (2007), in these article, discuss the 5thedition companies are increasingly employing financial System. A computer as they are made and the financial balance is the constantly revised. When the recorded point is reached, the computer automatically places an order, when this new order is received, the recorded balance is increased. Retail stores have carried this System quite far. Each item has magnetic codes, and as on item is checked out, it passes over an electronic reader, which then adjusts the computers financial balance, at the same time the price is fed to cash register tape. Fetch from (http://www.academia.edu/27763145/CHAPTER_II_Review_of_Related_Literature_and_Study_2.1_Review_of_Related_Literature_2.1.1_Foreign_Literature)
The researcher have learned that, financial system according to Bridgman when it increasingly the balance will constantly be revised. And when it reaches the maximum electronic reader it adjusts the computer financial balance and price fed to cash register tape.
Working Capital Management
According to (Garrison, 1999), Working Capital Management (WCM) refers to decisions relating to working capital and short term financing. These involve managing the relationship between a firm’s short-term assets and short-term liabilities. The goal of WCM is to ensure that the firm is able to continue its operations and that it has sufficient cash flow to satisfy both maturing short-term debt and upcoming operational expenses. The context of working capital management includes cash management, receivables and payables management. Fetch from (http://chss.uonbi.ac.ke/sites/default/files/chss/THE%20RELATIONSHIP%20BETWEEN%20FINANCIAL%20MANAGEMENT%20PRACTICES%20AND%20.pdf)
The researchers learned, that this foreign study according to (Garrison, 1999) that working capital management refers to some decision making, which involves payables and receivable and cash or budget management. In this case of study they’re some features will be add to our system.
Study of Recent Literature on Public Financial Management and Accountability (PFMA) System of the Government of India
This case study conducts a survey of the more recent literature on the public financial management and accountability system of the Government of India and analyzes its contents. The overall objective is to provide the basis for enhanced knowledge and understanding of the public financial management and accountability system including its strengths and weaknesses as perceived by the authors of the publications. The study prepares an annotated bibliography of select contemporary material on the public financial management and accountability system and presents an analytical survey relating to its various components. The study concludes that the legal systems are in place in all areas, as well as the attendant procedures, rules and regulations. Trained manpower is available. Oversight systems are vibrant through well-established independent external audit and legislative committees. There is increasingly more transparency in the budgetary disclosures. Steps have been taken to review the existing accounting systems. One area of concern is the compliance gap. There is found to be slackness in observing and enforcing the rules and regulations. Fetch from
https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/12522
The researchers learned that the (PMFA) or Public Financial Management Accountability the system was vibrant through well establish independent external audit and legislative committees. The PMFA they are also include the transparency in the budgetary disclosure. This process gives an idea to researcher on how to monitor the budget that could not be disclosed or over price.
Related Local Studies:
Manila Consensus on Public Financial Management (2011)
In this case of study of Manila Consensus on PFM contributed to shaping PFM-related commitments in Busan. It called on partner countries to be ambitious in strengthening their PFM systems through credible reform programmes, and urged development partners to increase the amount of external assistance flowing through a country’s PFM system as part of efforts to improve implementation of public policy and its results for sustainable development.
The Manila Consensus on Public Financial Management recognizes that: (i) more needs to be done at country level to support and strengthen PFM as an essential component of better economic governance; and (ii) international for a can assist in providing a peer review mechanism as well as a platform for knowledge sharing on strengthening and using country PFM systems. It sets out a number of commitments specifically focusing on PFM.
Strong public financial management (PFM) systems are essential for effective and sustainable economic management and public service delivery. States are effective and accountable when they are underpinned by good PFM institutions and systems. Good PFM systems are also indispensable in ensuring that aid is being used to achieve development goals.
http://www.oecd.org/dac/effectiveness/pfm.htm
The researchers learned that the Manila Consensus on Public Financial Management they are focusing on how the system become a credible reforms in programmes to develop the partners increase the external assistance flowing through the country’s. The system also improves the implementation of public policy and its result become sustainable. The researcher has an idea to add other features on the proposed system and that is the source of income.
Philippine Public Financial Management
The Public Financial Management (PFM) Reform Program aims to improve efficiency, accountability and transparency in public fund use in order to ensure the direct, immediate, substantial and economical delivery of public services especially to the poor.
The Program implements the key strategies of the Philippine PFM Reform Roadmap: Towards Improved Accountability and Transparency (2011-2016), a comprehensive reform agenda that seeks to clarify, simplify, improve and harmonize the government’s financial management processes and information systems. The integrated systems will cover all transactions of government and apply uniformly to all government agencies.
http://ro.uow.edu.au/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1462&context=aabfj
The researchers learned that Philippine Public Financial Management aims to improve their efficiency, accountability, and transparency in the fund in order to ensure the immediate, substantial and economical system that helps in the poor. This process help the researcher on how to make a efficiency and user friendly system that could be useful for the people.
Related Foreign System
Bureau of the Comptroller and Global Financial Services
The financial activities of the Department of State (the Department of DOS) occur in approximately 270 locations in 180 countries. We conduct business transaction in over 135 currencies and even more languages and cultures. Hundreds of financial and management professional around the globe allocate, disburse, and account for billions of dollars in annual appropriations, revenues, and assets. Among the Department’s customers are 45 U.S. Government agencies in every corner of the world, served 24 hours a day, seven days a week. The Department’s efforts are guided by two overarching goals: Providing world class financial services that support strategic decision-making, mission performance, and improved accountability and transparency to the American people; and supporting the achievement of the agency’s strategic goals by enabling interagency planning and coordination. Measures related to these goals include timely financial reporting, elimination of material weaknesses in internal control, the achievement if unmodified (“clean”) audit opinions, elimination of improper payments, and implementing resource management system and process that meet Federal requirements. In addition, the Department endeavors to consolidate and standardize financial operations, leverage best business practices and electronic technologies, and build a first rate finance team.
https://www.state.gov/s/d/rm/rls/perfrpt/2015/html/249759.htm
The researchers learned that the Bureau of the Comptroller and Global Financial Services focuses on managing the system process, payments the financial operations. This process gives the researchers on idea on how to monetize the system to avoid some conflict issues.
Financial management Information system a conceptual framework for Migori Country, kenya
In a modern world, developing countries like kenya, Tanzania, Ethiopia and several others in the African continent have been encouraged to reform their public expenditure management systems through computerization of the entire public sectors in response to the increasing volume of data or information that need to be processed. There are, however, various factors to be considered prior to the implementation of the public expenditure management information systems. This paper undertakes a theoretical review of the critical success factors that impact on the implementation of an integrated Financial management Information system (IFIMS) with a view to identify factors applicable to the Migori County of kenya. The paper, then, identifies the key factors to be incorporated in the proposed IFMS framework draws from the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), Innovation Diffusion theory(IDT) and the Work Around theory (WAT). The paper fuses these theories towards a successful adoption of use of modern technology within the public sector IFMS. The key factor includes technical, organizational, environmental, cultural and ethical behaviour. These factors could improve efficiency and transparency through direct payments to suppliers and contractors, reduced prices due to gains based on the time value of money, as well as the comparative analysis of market rates and advanced relations across the numerous organizational units within government on execution, reporting, and thoroughness of budget transactions.
The researcher learned that financial management Information system is focuses on the management of Information system. They proposed it for the computerization of the entire public sector in response to the increasing volume of data. Researchers conclude that management of information is very important on their proposed system that is very important is why we include it on the feature of our proposed system.
International Financial Architecture: Case Study – Russia
The Russian financial crisis of 1998 destabilized the international financial system and intensified the hardship experienced by the Russian people. This episode demonstrated that Russia in transition can be at once a carrier and victim of financial contagion. The experience of Russia and the other major emerging countries caught up in the financial market crises of 1997-98 has informed IMF-led attempts to develop codes and standards and measures for financial crisis prevention and cure as Part of a renewed ‘International Financial Architecture’ (IFA). This makes Russia an obviously central test case for evaluating the IFA project and identifying policy and technical assistance initiatives which could advance IFA goals. This report considers the Russian case history from two angles: Russian perspectives on IFA issues, and the extent of practical application of IFA standards in Russia in the context of broader policies designed to sustain the country’s post-crisis economic recovery. There is broad consensus among Russian economic officials in favours of IFA codes and standards, which are related to the central domestic economic policy objective of improving the investment climate. On the various international coordination and crisis prevention measures now under discussion, the Russian view tends to be mildly sceptical, with a stress on the value of traditional IMF programmed in providing member countries with technical expertise and investor confidence. At the same time, there are Russian sensitivities to take into account. These are reflected in the refusal to publish reports on standards and codes prepared last year by the IMF, and stem from the typical perception that these are demands aimed at Russia as a problem country rather than applied impartially as a measure of the transparency and quality of countries’ economic policies. There is a particular Russian suspicion that new standards might arbitrarily cut across more familiar IMF conditionality. In most areas of practical implementation of codes and standards, the picture is similar to that of broader structural reform: there is encouraging progress to report, along with much unfinished business. Examples of progress include data dissemination and capital markets regulation, while notable blockages remain in accounting reform and financial sector supervision and restructuring. Training should be the focus of any future technical assistance, following the lead of existing IMF training programmes. Besides enhancing growth-oriented policies, progress in implementation could have the specific benefit for Russia of reducing the cost of any market-based debt refinancing in the approaching debt service spike in 2003, when Official debt relief and new IFI lending cannot be counted on.
https://www.ids.ac.uk/ids/global/Finance/pdfs/IFACasestudyRussia1.pdf
The researchers learned that IMF focuses on the financial sector how to avoid financial sector problem on their process. This related literature helps the researcher to construct again new feature for their proposed system regarding financial management.
Related Local System
Shangri-Lathe Asset Management division of Shangri-La Asia Limited is responsible for ensuring that the company is generating the highest financial return possible from its owned hotel portfolio. The team further covers all hotel investment and development aspects of the company and assesses the viability of new projects and major renovations. Reporting to the Vice President – Asset Management, you will support management planning and decision making by identifying, maintaining, and evaluating information related to company’s strategic initiatives and financial performance; and make recommendations accordingly. Fetched From (https://www.jobable.com/shangri-la-hotels-jobs/hong-kong/manager-asset-management-79247-46803)
The researchers learned in this local system, it has a similar approach and features that will be applied and lessen the hassle in managing data.
Philippines – Public financial management and accountability assessment report: PFM strategy implementation support (English)
ABSTRACT
This case system study of Public Expenditure and Financial Accountability (PEFA) performance assessment report evaluates the seven core pillars of the public financial management (PFM) system of the Government of the Philippines (Government) as set out in the summary assessment below. It evaluates how effectively the PFM system achieves the desirable budget outcomes of aggregate fiscal discipline, strategic allocation of resources, and efficient service delivery. The assessment was conducted through consultations between departmental staff and a World Bank cross-sectored team, and was managed by a high-level Government steering committee. Where there are PFM weaknesses, the report provides information on areas that reform activity should address more strongly. The recent assessment uses an upgraded 2016 PEFA framework that includes four new indicators on management of assets and liabilities, refines some of the previous indicators, and introduces a stronger focus on internal financial controls. The main report is structured as follows: Chapter one is an introduction explaining the context, purpose and process of preparing the report, specifying the institutional coverage; Chapter two provides an overview of relevant country-related information that provides the context underpinning the indicator results and the overall PFM performance; Chapter three provides the detailed assessment of performance in terms of the seven pillars of the PFM system. It provides analysis and measurement of results in terms of the 31 performance indicators (PIs) of PFM performance; Chapter four includes an integrated crosscutting analysis on performance of the PFM systems and how it impacts on the Government’s ability to deliver on the intended fiscal and budgetary outcomes, and to identify the most important systems weaknesses in that respect; Chapter five provides an overview of government initiatives to improve PFM performance summarizing the approach to PFM reform, including the institutional factors that are likely to impact the planning and implementation of reforms. Annexes 1-4 provide supporting data and information to the assessment; and Annex 5 provides scores assessed using the 2005/2011 PEFA assessment framework for direct comparison with the previous PEFA assessment baseline scores.
The researchers learned that in this related literature on how to improve the proposed system based on the functionality of the system. By this the researcher can make the design and function that is unique for this system, and a user friendly system.
Prior Arts
Barangay Office Management System
A Barangay is considered as the smallest unit of the government in the Philippines. It performs the initial operations such as formation and employing of programs, activities, policies and other that involved the community. As the Philippines, population increases, the number of households in each barangay in the country increases.
Today, population continually upgrades those results into a growing number of labors especially the barangay Secretary, barangay treasurer, and barangay Clerk. The development of a barangay office management system enables the users to manage and print barangay citizen’s request and financial records and reports such as: payroll for honoraria and allowance, Disbursement Voucher, purchase orders, etc. (advancejournals.org)
The researchers learned that in this system in today’s population every day the technology upgrades and number of labors also increase. In this system connect to our proposed system have a similar approach to provide the citizen’s request and services.
Synthesis:
Based from the studies and systems that the researchers gather, to be able to develop a good and successive financial management system it is important to include new develop technology. For developing an accurate system, and by studying other system can help to develop a more complete and efficient system. Therefore the system should have a good database where the end-users can easily access with-out time consuming, make a request to the system in a short period of time, and record or store a data accurately. The researchers have some initial useful features that needed to be added in our barangay financial management system.
Credits to the authors and developers of the project/study
You may visit our facebook page for more information, inquiries and comments.
Hire our team to do the project.