Disaster Management Information System
Table of Contents
- Disaster Management Information System
- A Digital Solution for Faster and Smarter Emergency Response
- What Is a Disaster Management Information System?
- The Need for a Digital Disaster Management System
- 1. Delayed Information Flow
- 2. Poor Coordination
- 3. Lack of Real-Time Data
- 4. Resource Misallocation
- Core Objectives of a DMIS
- Key Features of a Disaster Management Information System
- 1. Incident Reporting Module
- 2. Real-Time Monitoring Dashboard
- 3. Resource Management System
- 4. Communication and Alerts
- 5. Evacuation and Shelter Management
- 6. Data Analytics and Reporting
- Phases of Disaster Management Supported by the System
- 1. Preparedness
- 2. Response
- 3. Recovery
- 4. Mitigation
- Benefits of a Disaster Management Information System
- Faster Decision-Making
- Improved Coordination
- Enhanced Public Safety
- Efficient Resource Allocation
- Better Transparency and Accountability
- Use Cases of the System
- Local Government Disaster Offices
- National Disaster Agencies
- Humanitarian Organizations
- Schools and Institutions
- Core System Modules
- 1. User and Role Management
- 2. Incident Management Module
- 3. Resource Management Module
- 4. Communication Module
- 5. Shelter and Evacuation Module
- 6. Reporting and Analytics Module
- Technology Stack
- Frontend
- Backend
- Database
- Mapping and Geolocation
- Security
- Integration Capabilities
- Weather Monitoring Systems
- SMS Gateway Services
- GIS Platforms
- Government Databases
- Challenges in Implementing a DMIS
- Infrastructure Limitations
- Training Requirements
- Data Accuracy
- System Maintenance
- Future of Disaster Management Systems
- Artificial Intelligence
- IoT Sensors
- Drone Integration
- Mobile-First Platforms
- Conclusion
A Digital Solution for Faster and Smarter Emergency Response
Natural and human-made disasters continue to pose serious threats to communities around the world. Floods, earthquakes, typhoons, landslides, fires, and health emergencies can cause widespread damage, disrupt livelihoods, and endanger lives. In many cases, the effectiveness of disaster response depends on how quickly and accurately information is gathered, analyzed, and shared among responders.
Traditional disaster response methods often rely on manual reporting, fragmented communication, and delayed coordination between agencies. These limitations can slow down decision-making and reduce the effectiveness of emergency operations.
A Disaster Management Information System (DMIS) provides a digital, centralized solution that helps government agencies, emergency responders, and organizations manage disasters more efficiently. By using real-time data, automated workflows, and integrated communication tools, the system improves preparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation efforts.
What Is a Disaster Management Information System?
A Disaster Management Information System is a web-based or mobile-enabled platform designed to collect, manage, analyze, and distribute information during all phases of disaster management. It acts as a centralized hub where authorities can monitor incidents, coordinate response activities, allocate resources, and communicate with stakeholders.
The system integrates various components such as:
- Incident reporting
- Resource tracking
- Situation monitoring
- Communication tools
- Data analytics and reporting
By consolidating these functions into a single platform, the system ensures faster response times and better coordination among agencies.
The Need for a Digital Disaster Management System
Many disaster-prone regions still rely on manual processes, spreadsheets, or disconnected systems to manage emergencies. These approaches present several challenges.
1. Delayed Information Flow
Manual reporting methods often result in slow data transmission from field personnel to command centers.
2. Poor Coordination
Multiple agencies may operate independently, leading to duplication of efforts or gaps in response.
3. Lack of Real-Time Data
Without live updates, decision-makers may rely on outdated or incomplete information.
4. Resource Misallocation
Inefficient tracking of supplies, personnel, and equipment can lead to shortages or wastage.
A digital disaster management information system addresses these issues by providing a unified, real-time platform.
Core Objectives of a DMIS
The primary goals of a disaster management information system include:
- Improving situational awareness
- Enhancing coordination among agencies
- Accelerating response times
- Optimizing resource allocation
- Providing accurate and timely information
- Supporting data-driven decision-making
Key Features of a Disaster Management Information System
1. Incident Reporting Module
Field personnel and community members can report disasters or emergencies through web or mobile interfaces. Reports may include:
- Incident type
- Location (GPS-enabled)
- Photos or videos
- Severity level
- Affected population
This information is instantly available to emergency coordinators.
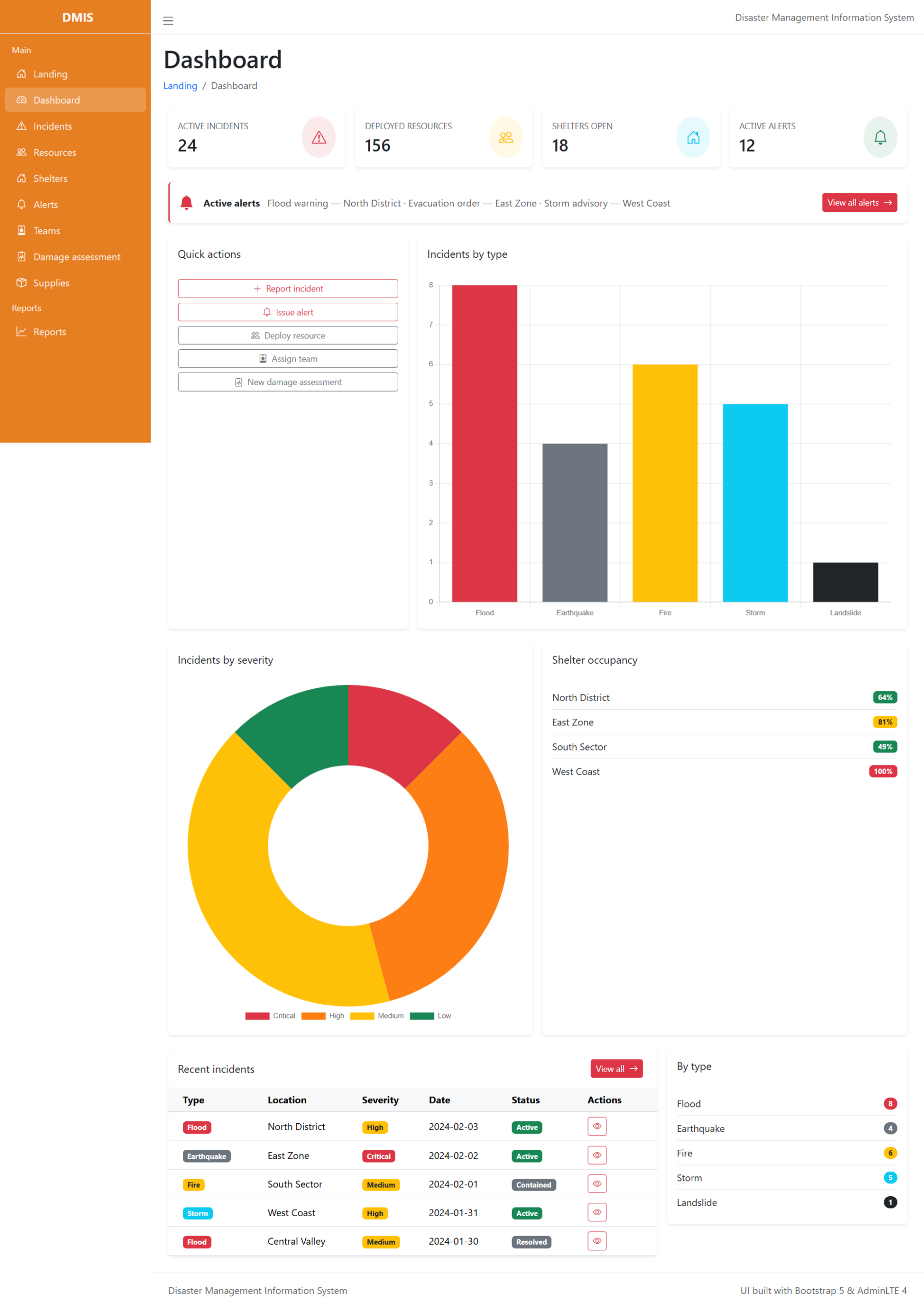
2. Real-Time Monitoring Dashboard
A centralized dashboard provides a live overview of all ongoing incidents. The dashboard may include:
- Interactive maps
- Incident status updates
- Weather alerts
- Resource availability
- Response team locations
This helps decision-makers quickly assess the situation.
3. Resource Management System
The system tracks available resources such as:
- Rescue teams
- Medical supplies
- Relief goods
- Vehicles and equipment
- Temporary shelters
Authorities can allocate resources based on real-time needs and priorities.
4. Communication and Alerts
The platform includes integrated communication tools to:
- Send emergency alerts
- Notify response teams
- Coordinate with agencies
- Broadcast public advisories
Notifications can be delivered through:
- SMS
- Mobile push notifications
- Web announcements
5. Evacuation and Shelter Management
The system helps manage evacuation centers by tracking:
- Occupancy levels
- Available supplies
- Health and sanitation conditions
- Evacuee registration
This ensures better planning and resource distribution.
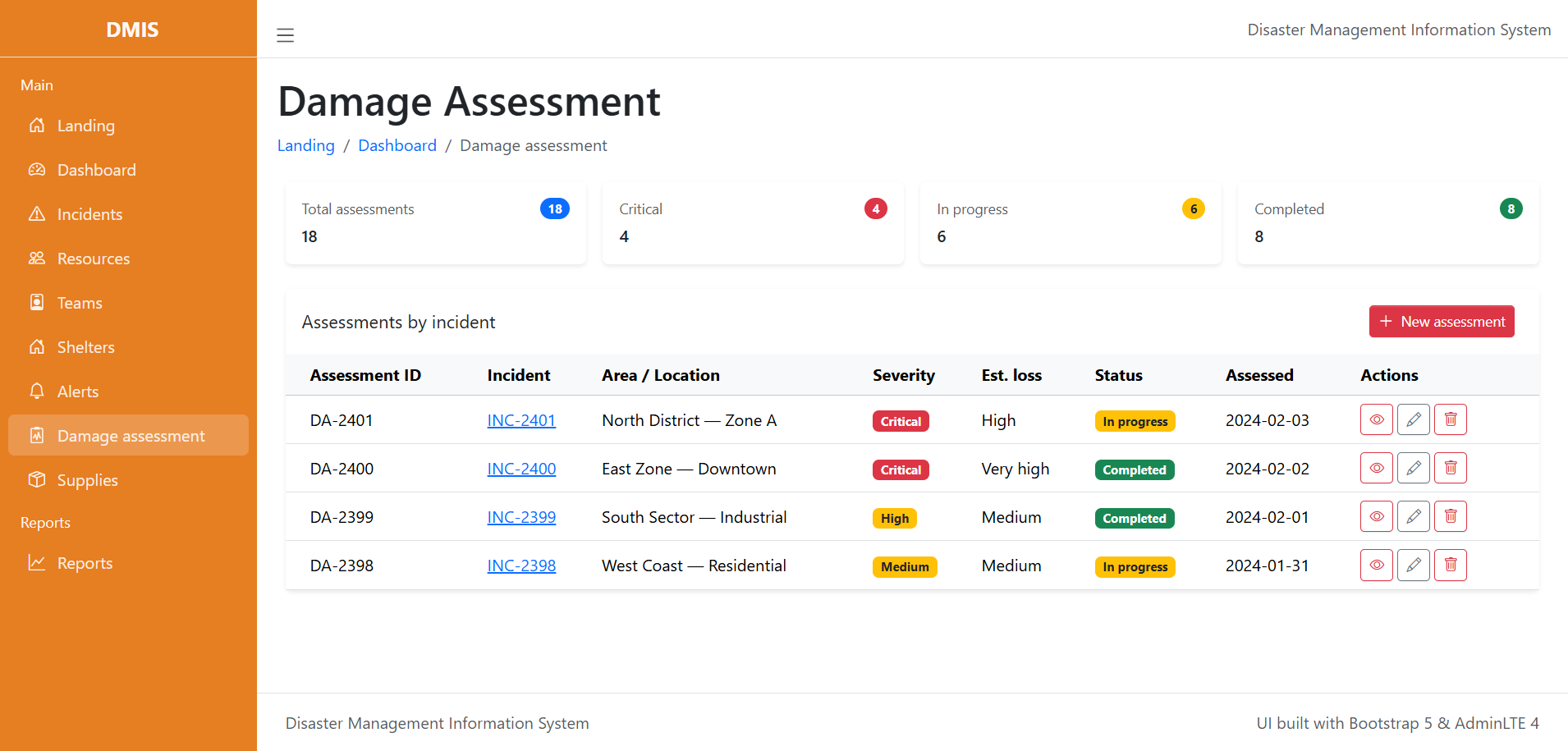
6. Data Analytics and Reporting
The system generates reports for:
- Incident trends
- Resource utilization
- Response times
- Damage assessments
These reports support strategic planning and post-disaster evaluations.
Phases of Disaster Management Supported by the System
A disaster management information system supports all four phases of disaster management.
1. Preparedness
Before disasters occur, the system helps agencies:
- Map risk-prone areas
- Plan evacuation routes
- Train personnel
- Conduct drills
- Maintain resource inventories
2. Response
During an active disaster, the system enables:
- Real-time incident reporting
- Rapid deployment of resources
- Coordination between agencies
- Communication with affected communities
3. Recovery
After the disaster, the system supports:
- Damage assessments
- Relief distribution tracking
- Infrastructure restoration planning
- Financial assistance management
4. Mitigation
In the long term, the system helps:
- Analyze disaster trends
- Identify high-risk areas
- Plan infrastructure improvements
- Develop preventive strategies
Benefits of a Disaster Management Information System
Faster Decision-Making
Real-time data allows authorities to make informed decisions quickly.
Improved Coordination
Multiple agencies can collaborate through a single platform.
Enhanced Public Safety
Faster alerts and response actions help protect lives.
Efficient Resource Allocation
Resources are distributed based on actual needs.
Better Transparency and Accountability
All actions and transactions are recorded within the system.
Use Cases of the System
Local Government Disaster Offices
LGUs can use the system to manage evacuation centers, monitor incidents, and coordinate response teams.
National Disaster Agencies
Central authorities can monitor disasters across regions and allocate resources accordingly.
Humanitarian Organizations
NGOs can track relief operations and coordinate with government agencies.
Schools and Institutions
Educational institutions can use the system for emergency preparedness and campus safety.
Core System Modules
A typical disaster management information system includes the following modules:
1. User and Role Management
- User registration and authentication
- Role-based access control
- Agency or department assignment
2. Incident Management Module
- Incident reporting
- Status tracking
- Location mapping
3. Resource Management Module
- Inventory tracking
- Personnel management
- Equipment allocation
4. Communication Module
- Alert system
- Messaging platform
- Notification management
5. Shelter and Evacuation Module
- Shelter registration
- Occupancy monitoring
- Evacuee tracking
6. Reporting and Analytics Module
- Incident reports
- Resource utilization reports
- Performance metrics
Technology Stack
A modern disaster management information system can be built using reliable and scalable technologies.
Frontend
- HTML5
- CSS3
- JavaScript
- Bootstrap
- AdminLTE dashboard template
Backend
- PHP, Python, or Node.js
- RESTful API architecture
Database
- MySQL or PostgreSQL
Mapping and Geolocation
- Google Maps API or open-source mapping tools
- GPS integration
Security
- SSL encryption
- Role-based access control
- Multi-factor authentication
Integration Capabilities
A DMIS can be integrated with other systems for enhanced functionality.
Weather Monitoring Systems
Receive real-time weather updates and alerts.
SMS Gateway Services
Send emergency notifications to residents.
GIS Platforms
Visualize disaster-prone areas and incident locations.
Government Databases
Access demographic and infrastructure data.
Challenges in Implementing a DMIS
Infrastructure Limitations
Some areas may lack reliable internet or power during disasters.
Training Requirements
Personnel need proper training to use the system effectively.
Data Accuracy
Incorrect or delayed data entry can affect decision-making.
System Maintenance
Regular updates and technical support are required.
Future of Disaster Management Systems
With advancements in technology, future disaster management systems may include:
Artificial Intelligence
AI can predict disaster patterns and suggest response strategies.
IoT Sensors
Connected sensors can monitor environmental conditions in real time.
Drone Integration
Drones can provide aerial assessments of disaster zones.
Mobile-First Platforms
Offline-capable mobile apps can support field responders.
Conclusion
A Disaster Management Information System is an essential digital tool for modern emergency response and preparedness. By centralizing information, automating workflows, and enabling real-time coordination, the system significantly improves disaster management operations.
From incident reporting and resource allocation to evacuation management and data analytics, the platform ensures that authorities can respond quickly and effectively during emergencies. As disasters become more frequent and complex, investing in a reliable disaster management information system is critical for protecting lives, property, and communities.
You may visit our Facebook page for more information, inquiries, and comments. Please subscribe also to our YouTube Channel to receive free capstone projects resources and computer programming tutorials.
Hire our team to do the project.